python 3.10?
for ERPNext v15 you need 3.11+ as far as I know
This is a bench playbook error caused by a recent ansible update.
Go to this file:
/usr/local/lib/python${python_version}/dist-packages/bench/playbooks/roles/mariadb/tasks/main.yml
Change include to include_tasks and re-run sudo bench setup production $USER and your installation should be completed.
You can also use the script i shared above for installation.
I could run the install script yesterday but with many errors.
@flexy2ky , I raised an issue ticket on github, as it seems that there are others have the same issue, fyki, i also purchased a vps on contabo and tried your script and it suddenly closes the putty/bitvise terminal screen.
thanks for your support
Thanks for flagging the issue. Please refer to my response on GitHub. Thanks
Getting Error on step 5. Please Help
sudo pip3 install frappe-bench
error: externally-managed-environment
× This environment is externally managed
╰─> To install Python packages system-wide, try apt install
python3-xyz, where xyz is the package you are trying to
install.
If you wish to install a non-Debian-packaged Python package,
create a virtual environment using python3 -m venv path/to/venv.
Then use path/to/venv/bin/python and path/to/venv/bin/pip. Make
sure you have python3-full installed.
If you wish to install a non-Debian packaged Python application,
it may be easiest to use pipx install xyz, which will manage a
virtual environment for you. Make sure you have pipx installed.
See /usr/share/doc/python3.11/README.venv for more information.
note: If you believe this is a mistake, please contact your Python installation or OS distribution provider. You can override this, at the risk of breaking your Python installation or OS, by passing --break-system-packages.
hint: See PEP 668 for the detailed specification.
To disable the externally-managed-environment error
sudo python3 -m pip config --global set global.break-system-packages true
Got an error at bench init frappe-bench --version $bench_version --verbose:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/bin/bench", line 8, in <module>
sys.exit(cli())
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/bench/cli.py", line 74, in cli
cmd_from_sys = get_cmd_from_sysargv()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/bench/utils/__init__.py", line 581, in get_cmd_from_sysargv
if sys_argv.index(arg) == 0 and arg in Bench(".").apps:
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/bench/bench.py", line 67, in __init__
self.apps = BenchApps(self)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/bench/bench.py", line 175, in __init__
self.initialize_apps()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/bench/bench.py", line 282, in initialize_apps
self.apps.remove("frappe")
ValueError: list.remove(x): x not in list
An error occurred on line 351 with exit status 0
Trying to reinstall the system.
I think this happened because I updated the Ubuntu 22.04.4 installer during installation.
Tried three times, eventually without updating the installer.
Problem solved(?)
sudo bench setup production [frappe-user] might not work if you don’t do the following!!
error (deprecated): ansible.builtin.include has been removed
Solution
-
sudo nano /usr/local/lib/python3.1/dist-packages/bench/playbooks/roles/mariadb/tasks/main.yml
-
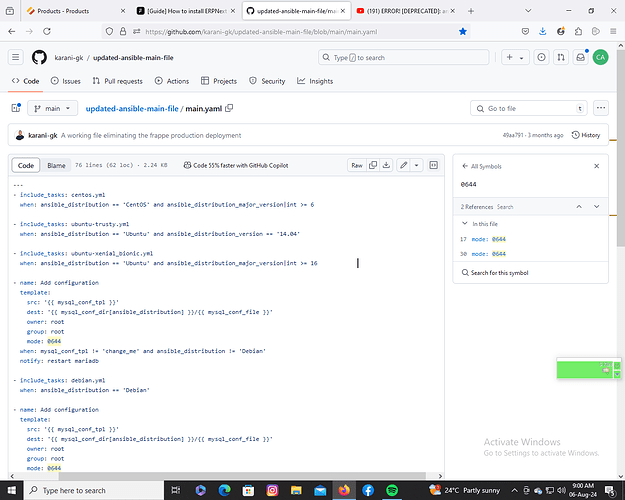
copy the following code below (updated-ansible-main-file/main.yaml at main · karani-gk/updated-ansible-main-file · GitHub)
-
include_tasks: centos.yml
when: ansible_distribution == ‘CentOS’ and ansible_distribution_major_version|int >= 6 -
include_tasks: ubuntu-trusty.yml
when: ansible_distribution == ‘Ubuntu’ and ansible_distribution_version == ‘14.04’ -
include_tasks: ubuntu-xenial_bionic.yml
when: ansible_distribution == ‘Ubuntu’ and ansible_distribution_major_version|int >= 16 -
name: Add configuration
template:
src: ‘{{ mysql_conf_tpl }}’
dest: ‘{{ mysql_conf_dir[ansible_distribution] }}/{{ mysql_conf_file }}’
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
when: mysql_conf_tpl != ‘change_me’ and ansible_distribution != ‘Debian’
notify: restart mariadb -
include_tasks: debian.yml
when: ansible_distribution == ‘Debian’ -
name: Add configuration
template:
src: ‘{{ mysql_conf_tpl }}’
dest: ‘{{ mysql_conf_dir[ansible_distribution] }}/{{ mysql_conf_file }}’
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0644
when: mysql_conf_tpl != ‘change_me’ and ansible_distribution == ‘Debian’
notify: restart mariadb -
name: Add additional conf for MariaDB 10.2 in mariadb.conf.d
blockinfile:
path: /etc/mysql/conf.d/settings.cnf
block: |
# Import all .cnf files from configuration directory
!includedir /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/
become: yes
become_user: root
when: ansible_distribution == ‘Ubuntu’ or ansible_distribution == ‘Debian’ -
name: Add additional conf for MariaDB 10.2 in mariadb.conf.d
blockinfile:
path: /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/erpnext.cnf
block: |
[mysqld]
pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock# setting appeared inside mysql but overwritten by mariadb inside mariadb.conf.d/xx-server.cnf valued as utf8mb4_general_ci collation-server = utf8mb4_unicode_cicreate: yes
become: yes
become_user: root
when: ansible_distribution == ‘Ubuntu’ or ansible_distribution == ‘Debian’ -
name: Start and enable service
service:
name: mariadb
state: started
enabled: yes -
debug:
msg: “{{ mysql_root_password }}” -
include_tasks: mysql_secure_installation.yml
when: mysql_root_password is defined -
debug:
var: mysql_secure_installation
when: mysql_secure_installation and mysql_root_password is defined
…
-
Paste into main.yml file located at /usr/local/lib/python3.1/dist-packages/bench/playbooks/roles/mariadb/tasks/
-
Now you can run sudo bench setup production [frappe-user] successfully without errors.
nice guideline, I appreciate this
Thanks - I installed frappe ‘as’ the same user I was running it with - it’s a dev server, but you STILL have to execute this step.
== John ==
This needs to be documented (or fixed!)
Appreciate it!
Here’s one for you:
Why do we need xvfb?
It has a s##t load of dependancies.
What does it do? Do we actually use an X server at all?
Thank you for this. Was able to install without any sort of errors. With other guides i always stumble upon an error and it eats up hours.
Only problem was with HRMS.
try installing HRMS after setting production env.
List the files and directories within the ‘assets’ folder with detailed information (permissions, owner, size, etc.)
ls -l /home/[user]/frappe-bench/sites/assets
Change to the ‘assets’ directory, where the public files of the apps are located
cd /home/[user]/frappe-bench/sites/assets
Remove existing symbolic links if they are incorrect or need to be updated.
Make sure to check if these apps are installed before removing them. These lines may vary depending on your installation.
rm frappe erpnext # Remove symbolic links for Frappe and ERPNext (commonly installed)
rm lms hrms # Optional: Only remove if you have LMS or HRMS apps installed
Create new symbolic links pointing to the correct public directories of the installed apps.
Adjust the paths according to your app locations.
ln -s …/…/apps/frappe/frappe/public frappe # Symbolic link for Frappe (required if using Frappe)
ln -s …/…/apps/erpnext/erpnext/public erpnext # Symbolic link for ERPNext (required if using ERPNext)
Optional: Only create these links if you have LMS or HRMS installed
ln -s …/…/apps/lms/lms/public lms # Symbolic link for LMS (optional, only if using LMS)
ln -s …/…/apps/hrms/hrms/public hrms # Symbolic link for HRMS (optional, only if using HRMS)
Recursively change the owner and group of all files inside frappe-bench.
Replace [user] with your actual username.
sudo chown -R [user]:[user] /home/[user]/frappe-bench
Set read and execute permissions for all directories under ‘sites’. Permissions 755 (read and execute for all, write only for the owner)
sudo find /home/[user]/frappe-bench/sites -type d -exec chmod 755 {} ;
Set read permissions for all files under ‘sites’. Permissions 644 (read for all, write only for the owner)
sudo find /home/[user]/frappe-bench/sites -type f -exec chmod 644 {} ;
Add the web server user (e.g., ‘www-data’ for Nginx/Apache) to the current user’s group
Replace [user] with your actual username.
sudo usermod -a -G [user] www-data
Reload Nginx to apply the changes without restarting the service completely
sudo service nginx reload
Refers to tons of guides available on internet, everyone have to be very careful. The best option is refers to official documentation. Read carefully and make yourself well understand. Especially in case you will SELL yor skill to a client. For sure well understanding about software itself ( in this case is erpnext ), the server ( Just learn deeply one or two Linux distro ) operating system, linux is majority on server.
The guide is OK, work well, however since you will serve a client, you need to bring your skill to higher level, thus you can tackle problem, have skill on hand for trouble shouting.
Afaik, once the system set up, everything went well. Internal server error message, having many reasons : most problem due to update the OS. We have to understand the OS behaviour.
For example Debian ( I think, as well as ubuntu ), Tighten Mariadb to their basic system ( hardcoded ), user root for Mariadb should not be touched, due to upon OS update, they set configuration to “default”. If someone tocuhed the root user ( by default No Password ) and only accessed via system root user ( Your root user of OS ). Therefore it is wise, to create another root user for ERPNEXT or other application requiring root access to DB.
In case, your client deploy ERPNEXT on VPS, it will be easiser since one VPS system host only one application. However in case you deploy into physical server ( bare metal server ) which is always expensive and on the server host more than one application. The way of deployment must be different.
The guide is fit for deploy erpnext on VPS, with only erpnext hosted.
I have read a lot of guide with option : –break-system,-packages, imo, this is not wise. Breaking system packages is very risky on OS update process and potentially causing problem.
Learn, learn and learn, then patient and careful is better.
Ubuntu LTS, as well as Debian gives you a few years of silence, in “breaking system” terms. that been said, using a docker container (either only for the MariaDB, or, even better, for the whole deployment), means you have a lot more control (as I would guess VPS can give you).
Regarding hosting different applications\companies, it’s even simpler, by introducing a revers proxy to the mix, where all you need to do is direct it to a different port, that corresponds an app or a company. This way you can self host many clients’ servers yourself, and bill them for this (if this is your “shtick”, I would rather leave the client with the hosting part, where they have control).
I think containerizing is the simplest, and most efficient path for anyone who wishes to “sell their skills”. You don’t have to be a Linus Torvalds to help your clients, as long as your path for install is good (thus containers, a complete server image, or even a good install script, should be enough).
However, never stop learning… ![]()