Hello all
Due to the amount of posts on this forum about not getting REST / RPC calls to work when using parameters such as fields= and filters=, especially when using cURL, I’ve decided to give back a small contribution, making hopefully a HUGE difference in someone else’s life. Most of those posts remain unsolved, and so, with this tutorial I trust the opensource ERPNext community will go from strength to strength!
I assume you’ve set up token based authentication : user guide to do so
For further clarification on setting up token based authentication, please see the latter part of this thread, especially the posts by @MartinHBramwell
I’m testing the below cURL commands having created an API Access token on the Administrator user, which is probably not a good idea, but for testing purposes we’ll do that for now. Ideally you should create a user specifically for REST access.
I’m on Linux, so I’ll use Bash as my shell. Let’s assign your token to a shell variable, HT means Header Token.
HT='Authorization: token <your API key>:<your API secret>'
Let’s assign two more headers to shell variables, HA means Header Accept and HC means Header Content.
HA='Accept: application/json'
HC='Content-Type: application/json'
To test access to the HTTP API of your server, in your web browser’s URL bar type:
http://<url_or_ip_of_your_server>/api/method/frappe.handler.version
Note that your protocol could be https rather than http. The above frappe.handler.version is actually a RPC (not a REST) call, however it does not require authentication, so we can test whether our URL is correct. You should get back a JSON string such as
{"message":"12.15.0"}
Now let’s assign the URL to a shell variable. Note that the path to RPC endpoints is …/api/method/, but because we’re going to play around with REST calls first, the path is …/api/resource/ and we’ll call our shell variable UR meaning URL Resource.
UR='http://<url_or_ip_of_your_server>/api/resource/'
REST GET calls
-
Let's test a REST call using cURL, which does require authentication
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -X GET ${UR}UserYou should get back a JSON string such as
{"data":[{"name":"Administrator"},{... -
So far so good.
However, cURL does offer something called URL globbing. From the man page we read that globbing uses the { } and characters. This means that our REST calls cannot use parameters such as fields=[“name”] without being interpreted as globbing characters. So to provide a URL containing these characters you need to disable globbing with the -g option.
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -X GET -g ${UR}'User?fields=["name","email"]'…and voila! A REST call with a fields= parameter
{"data":[{"name":"Administrator","email":"admin@example.com"},{...Let’s add a filter= parameter
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -X GET -g ${UR}'User?fields=["name","email"]&filters=[["name","=","Administrator"]]'You should get only the Administrator as a result
{"data":[{"name":"Administrator","email":"admin@example.com"}]}or alternatively try escaping the " characters within the URL string
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -X GET -g "${UR}User?fields=[\"name\",\"email\"]&filters=[[\"name\",\"=\",\"Administrator\"]]" -
But there's a better way...
Instead of suffixing the parameters to the URL, we can supply the parameters as data using the -G and -d options. In this case we do not have to concern ourselves with the globbing conflict as the parameters are no longer part of the URL.
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -G "${UR}User" -d 'fields=["name","email"]' -d 'filters=[["name","=","Administrator"]]' - As a final titbit, note that the field references can be either the field name (aka ID) or the label, and even mixed, eg Name and email. They can even be mixed within the fields= and filters= parameters, eg Name and name. I'm not sure how robust this is, and it's probably better to use either the name or label consistently.
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -G "${UR}User" -d 'fields=["Name","email"]' -d 'filters=[["name","=","Administrator"]]'
REST POST and PUT calls
-
Create a new Lead record with a POST call
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -X POST ${UR}Lead -d '{"lead_name":"My-New-Lead"}'{"data":{"name":"CRM-LEAD-2021-00001","owner":"Administrator",... -
Update the contact_date of this new record with a PUT call. To avoid a
frappe.exceptions.ValidationError: Next Contact Date cannot be in the pasterror, make sure the date is in the future.
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -X PUT ${UR}Lead/CRM-LEAD-2021-00001 -d '{"contact_date":"2021-12-31"}' -
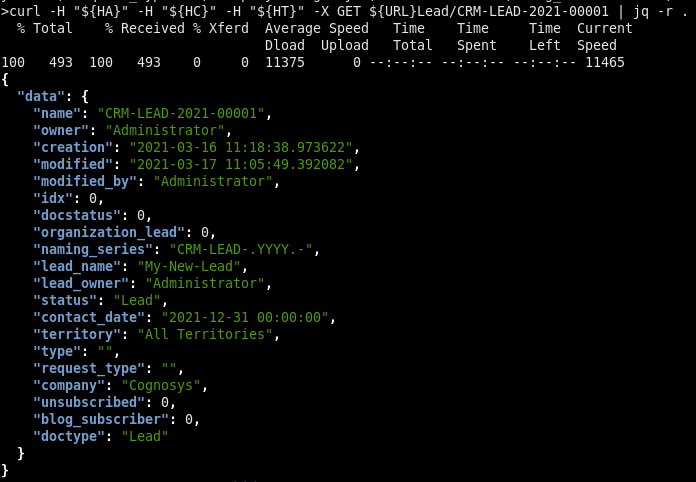
View the newly created record along with the change you've made to the contact_date. Note that I pipe the output to jq
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -X GET ${UR}Lead/CRM-LEAD-2021-00001 | jq -r .
RPC methods
There are a few idiosyncratic differences when it comes to how we need to structure our cURL RPC vs REST invocations. But first, let's create a new shell variable for the RPC endpoints.
UM='http://<url_or_ip_of_your_server>/api/method/'
-
To invoke an RPC which takes an argument, add it as a query parameter, ie suffix it after a ?
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -X GET ${UM}frappe.client.get_list?doctype=User -
However, I could not supply multiple arguments to an RPC by separating them with an &, but I am successful when I specify them as data, using the -G and -d options. Let's add the fields as our second argument.
curl -H "${HA}" -H "${HC}" -H "${HT}" -G ${UM}frappe.client.get_list -d 'doctype=User' -d 'fields=["name","full_name"]'Note that unlike for REST calls, field references in RPC methods only allow the name (aka ID) not also the label, ie “full_name” and not “Full Name”
Thanks to @revant_one for providing us with a convenient list of all whitelisted endpoints
That’s all from me ![]()